Most Shopify stores in Pakistan don’t lose sales because of pricing, traffic, or product quality. They lose them after checkout, in the hours when customers are waiting for confirmation, clarification, or reassurance.
That gap exists because e-commerce systems were built around email, while Pakistani customers operate on WhatsApp. The disconnect creates delays, cancellations, and unnecessary support load. So, this isn’t about team inefficiency, but because the communication layer is misaligned.
This is where WhatsApp API with Shopify in Pakistan sorts out your problems. It doesn’t act as a messaging tool, but as a transactional bridge between store events and customer expectations.
Understanding how this bridge works, technically and operationally, is what separates scalable stores from fragile ones.
Table of Contents
Does WhatsApp API Work in Pakistan? Infrastructure & Policy Reality

From a technical standpoint, WhatsApp Business API works in Pakistan because:
WhatsApp servers and message routing are globally managed by Meta.
Message delivery does not depend on local telecom SMS gateways
WhatsApp numbers in Pakistan are treated the same as any other supported region
However, availability is not the same as usability.
WhatsApp API access in Pakistan requires:
A registered phone number (not previously used on WhatsApp)
An official Business Solution Provider (BSP)
Template-based outbound messaging
This structure exists to prevent spam and protect end users. Any tool claiming “no approval needed” or “instant bulk messaging” is operating outside Meta policy. And accounts using such tools are statistically far more likely to be restricted or banned.
So yes, WhatsApp API works in Pakistan, but only when implemented within Meta’s approved framework.
How to Spot a Fake WhatsApp Business API Provider: 5 Red Flags to Watch
Why WhatsApp API Outperforms Email and SMS in Pakistan?
This is not about trends. It’s about channel mechanics and user behavior.
1- Visibility and Latency
- Email is asynchronous and often delayed.
- SMS lacks context, formatting, and interactivity.
- WhatsApp messages are delivered instantly and appear alongside personal conversations.
There are roughly 190 million active mobile connections in Pakistan, covering about 75% of the population
In Pakistan, where mobile-first usage dominates, WhatsApp becomes the fastest path from system to customer attention.
2- Trust Economics
E-commerce trust in Pakistan is fragile due to:
- High COD dependency
- Fraud history
- Inconsistent delivery experiences
WhatsApp creates a two-way verification channel:
- Customers can reply
- Ask questions
- Confirm intent
This interaction reduces perceived risk, which directly influences conversion and delivery success.
How does WhatsApp API integrate with Shopify?
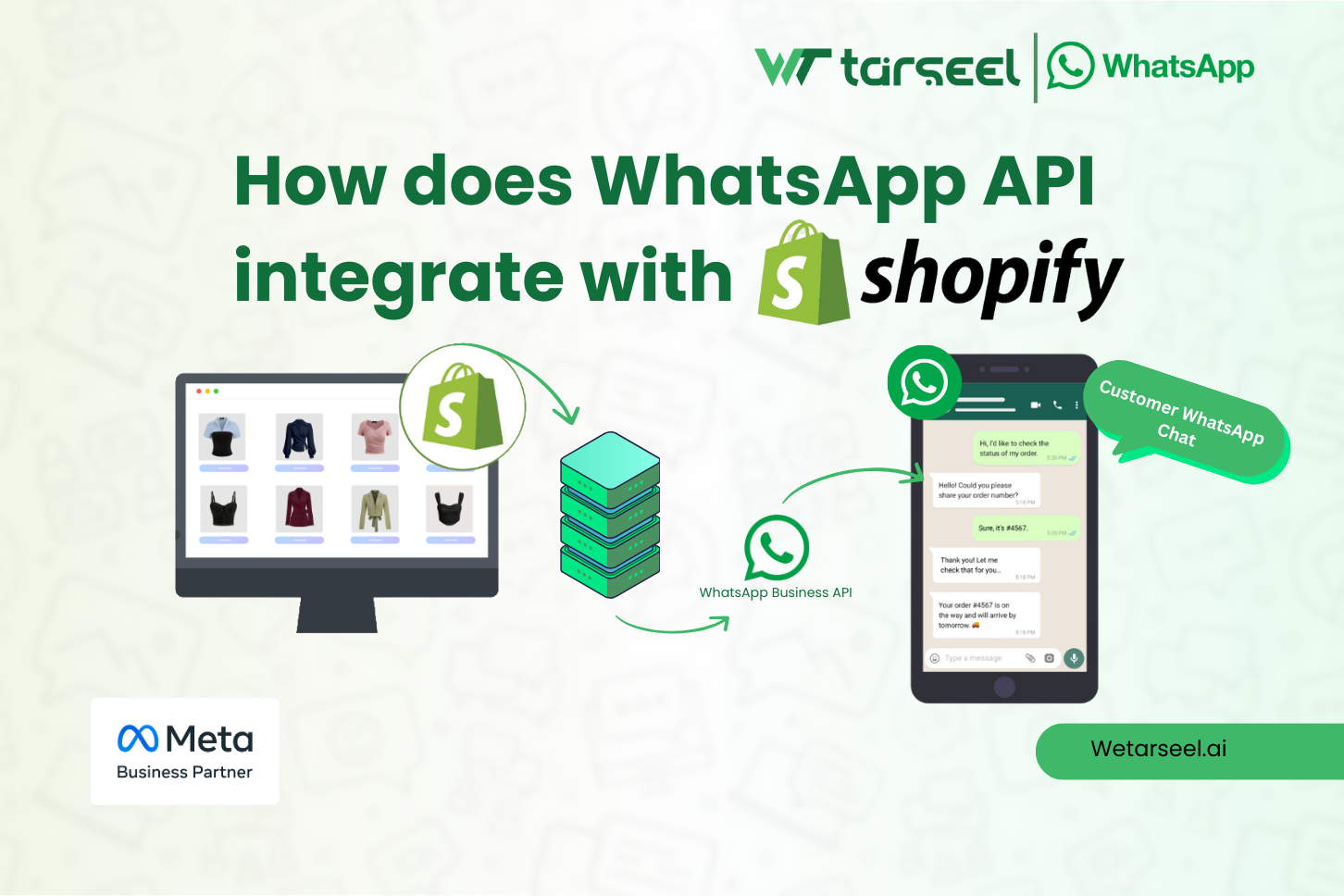
Shopify does not provide a native or built-in connection to the WhatsApp Business API. Instead, WhatsApp automation is implemented through an event-driven integration layer that sits between Shopify and Meta’s WhatsApp infrastructure.
This design is intentional.
Shopify is an e-commerce platform, WhatsApp is a messaging platform, and the two communicate through webhooks, APIs, and middleware logic rather than a direct point-to-point connection.
1. Shopify as the Event Source
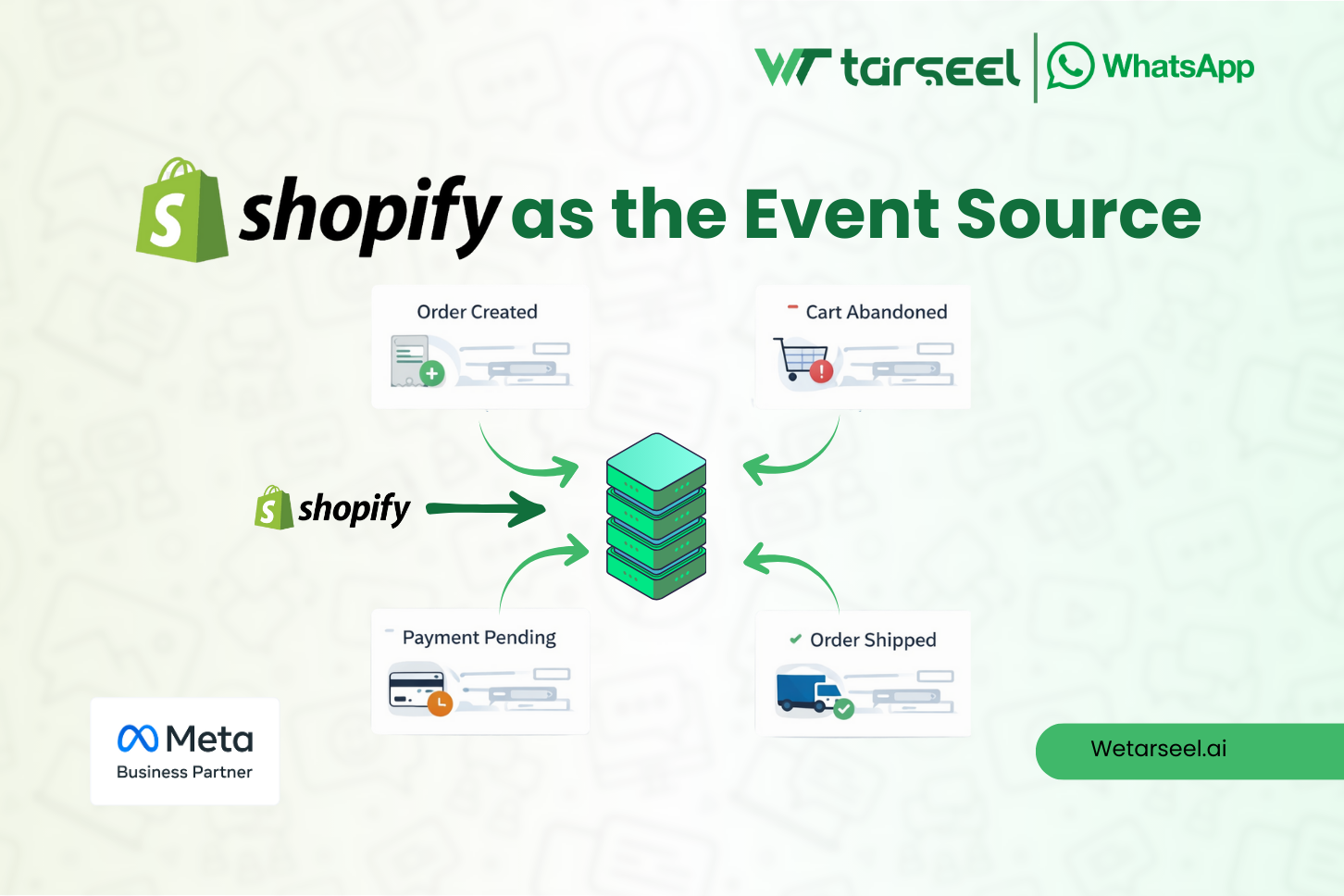
Shopify continuously generates structured events whenever meaningful actions occur in the store. Common examples include:
- Order creation
- Checkout abandonment
- Payment status updates
- Fulfillment and shipping changes
Each of these events represents a state change inside Shopify. On their own, they do nothing, but they become powerful once exposed via webhooks.
2. Webhooks: Real-Time Data Dispatch
Shopify webhooks act as real-time notifications. When a subscribed event occurs, Shopify sends a JSON payload to a predefined endpoint.
This payload typically includes:
- Customer phone number (if collected at checkout)
- Order and checkout identifiers
- Line items and quantities
- Payment method (COD, prepaid, etc.)
- Fulfillment or shipping status
The webhook ensures that communication is event-driven, not scheduled, which is critical for time-sensitive messaging like order confirmations or cart recovery.
3. API Processing & Business Logic Layer
The webhook payload is received by an integration layer (often provided by a WhatsApp API platform or a custom backend). This layer performs several essential tasks:
- Payload validation
Ensures data completeness, correct formatting, and phone number normalization. - Conditional logic execution
Determines whether a message should be sent.
Examples:Send COD confirmation only for cash-on-delivery orders
Skip abandoned cart messages if payment was completed later
Delay shipping updates until fulfillment is marked complete
Template selection
Maps the event type to the correct WhatsApp message template.
This step is where operational intelligence lives. Without it, WhatsApp messaging becomes noisy, repetitive, or non-compliant.
Using a Shopify App as the Integration Layer
In practice, most Shopify merchants do not build this integration layer from scratch. Instead, they use a Shopify app that already implements webhook ingestion, logic handling, and WhatsApp API connectivity in a compliant way.
For example, the Wetarseel WhatsApp Shopify app acts as this middleware layer by:
- Subscribing to Shopify events (orders, abandoned checkouts, fulfillment updates)
- Processing webhook payloads securely
- Applying predefined automation logic
- Triggering approved WhatsApp templates through the WhatsApp Business API
Because the app is installed directly from the Shopify App Store, it follows Shopify’s app security, permission, and data access standards.
Merchants who want to implement this approach can install the app from the Shopify App Store:
https://apps.shopify.com/whatsapp-wetarseel
This allows stores to deploy WhatsApp automation without maintaining custom backend infrastructure, while still operating within Meta and Shopify compliance requirements.
4. WhatsApp Business API Message Delivery
Once logic is applied, the system sends a request to the WhatsApp Business API, referencing:
- A pre-approved message template
- Dynamic variables (customer name, order ID, tracking URL)
- The recipient’s WhatsApp-enabled phone number
Template enforcement is mandatory. WhatsApp does not allow free-form outbound messages outside the customer service window. This ensures:
- Policy compliance
- High deliverability
- Protection against spam
Why This Architecture Matters
This integration model ensures:
- Zero manual intervention
Messages are triggered automatically by store activity. - Predictable and timely delivery
Notifications are sent when events happen, not hours later. - Policy-compliant scaling
Every message follows Meta’s rules, reducing the risk of bans or throttling.
In other words, WhatsApp API with Shopify is not a “plugin feature” but an event-driven communication system layered on top of your ecommerce operations.
Expert Insight
Most failed WhatsApp implementations don’t fail because of WhatsApp or Shopify. They fail because:
- Business logic is missing
- Templates are poorly designed
- Compliance is treated as optional
- Automation is added without understanding store workflows
Platforms like Wetarseel fit naturally into this architecture by handling webhook ingestion, logic evaluation, and compliant WhatsApp delivery, allowing Shopify stores to automate communication without breaking operational discipline.
Why the WhatsApp Business App Cannot Support Shopify Automation
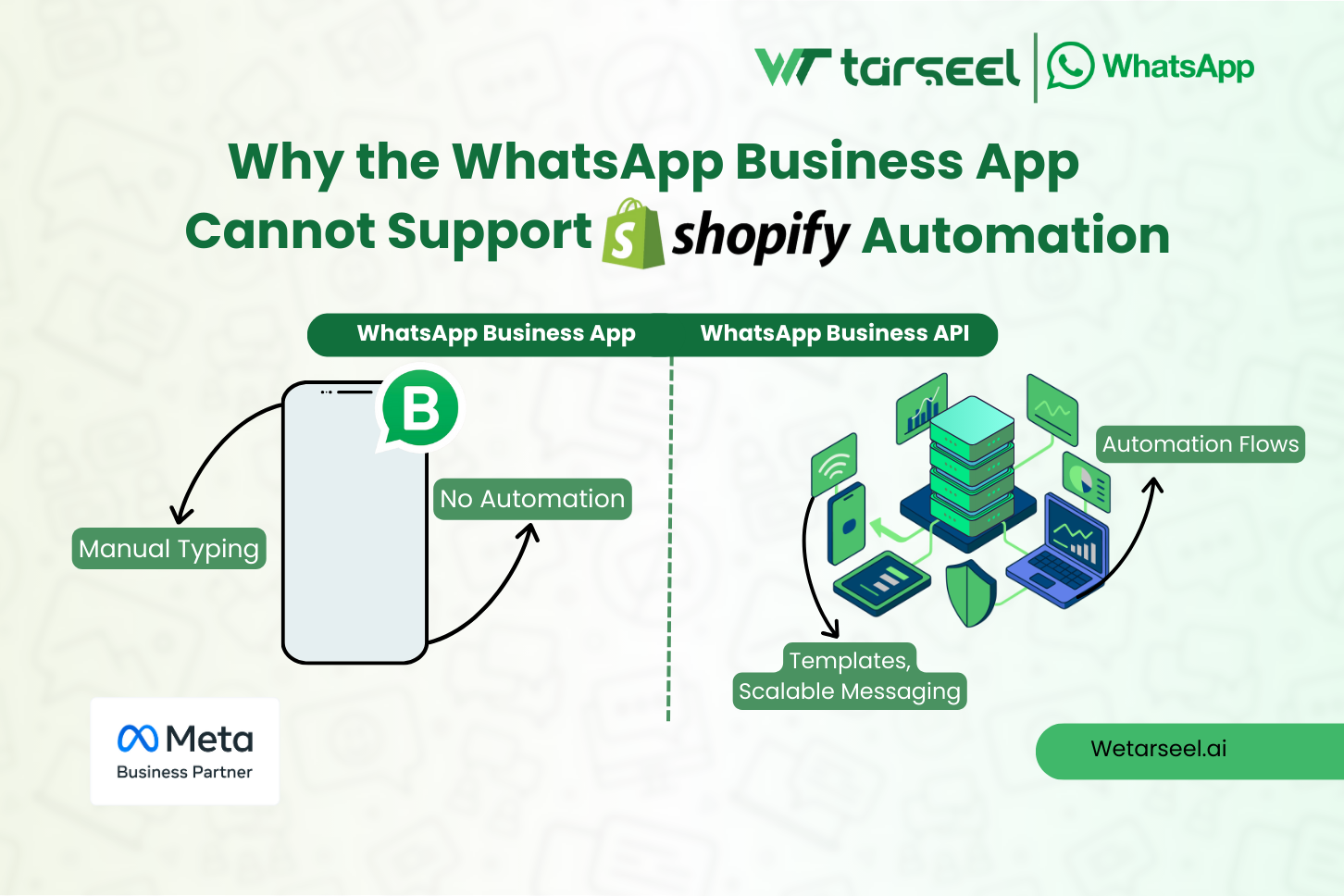
In the previous section, we explained how Shopify automation relies on events, webhooks, logic layers, and templates.
The WhatsApp Business App cannot participate in that architecture, not due to missing features, but due to how it is fundamentally designed.
The Business App is a standalone mobile application, built for human-to-human interaction. Shopify automation, on the other hand, requires system-to-system communication. That mismatch creates hard technical limitations.
1. No Ability to Receive Store Events
Shopify automation begins when store events occur (order placed, cart abandoned, fulfillment updated).
The Business App has no mechanism to receive or process these events because:
- It exposes no webhook endpoints
- It cannot accept incoming API calls
- It has no background process listening for triggers
As a result, it cannot react to Shopify activity automatically.
2. No Logic or Decision-Making Layer
Automation requires decisions, not just messages.
Examples:
- Send a COD confirmation only for cash-on-delivery orders
- Avoid cart reminders if checkout is completed later
- Delay shipping notifications until fulfillment is confirmed
The Business App has:
- No conditional logic
- No workflow engine
- No rule evaluation capability
Every message must be manually initiated, which breaks down as volume grows.
3. No Message Queuing or Load Management
When order volume spikes, automated systems queue messages to ensure:
- Correct sequencing
- Controlled sending rates
- Reliable delivery
The Business App sends messages interactively, one action at a time. It cannot:
- Queue outbound messages
- Handle traffic bursts
- Maintain predictable delivery timing
This makes it unsuitable for high-volume ecommerce communication.
4. No Template Governance for Automated Messaging
WhatsApp enforces template approval for automated outbound communication to protect users from spam.
The Business App bypasses this only because it is intended for manual conversations, not automation. As a result:
- There is no template governance
- No consistency enforcement
- No scalable compliance framework
This becomes a risk when businesses attempt to automate outside the API.
Why the WhatsApp Business API Is Required Instead
The WhatsApp Business API is not an alternative interface, it is a different product category altogether.
It is designed to:
- Accept event-triggered instructions
- Apply business logic before messaging
- Enforce template-based compliance
- Scale predictably as message volume grows
This is why the API fits naturally into the integration architecture explained earlier, and why the Business App cannot be “extended” to behave the same way.
High-Impact Automation Use Cases
1- Order Confirmation & COD Verification
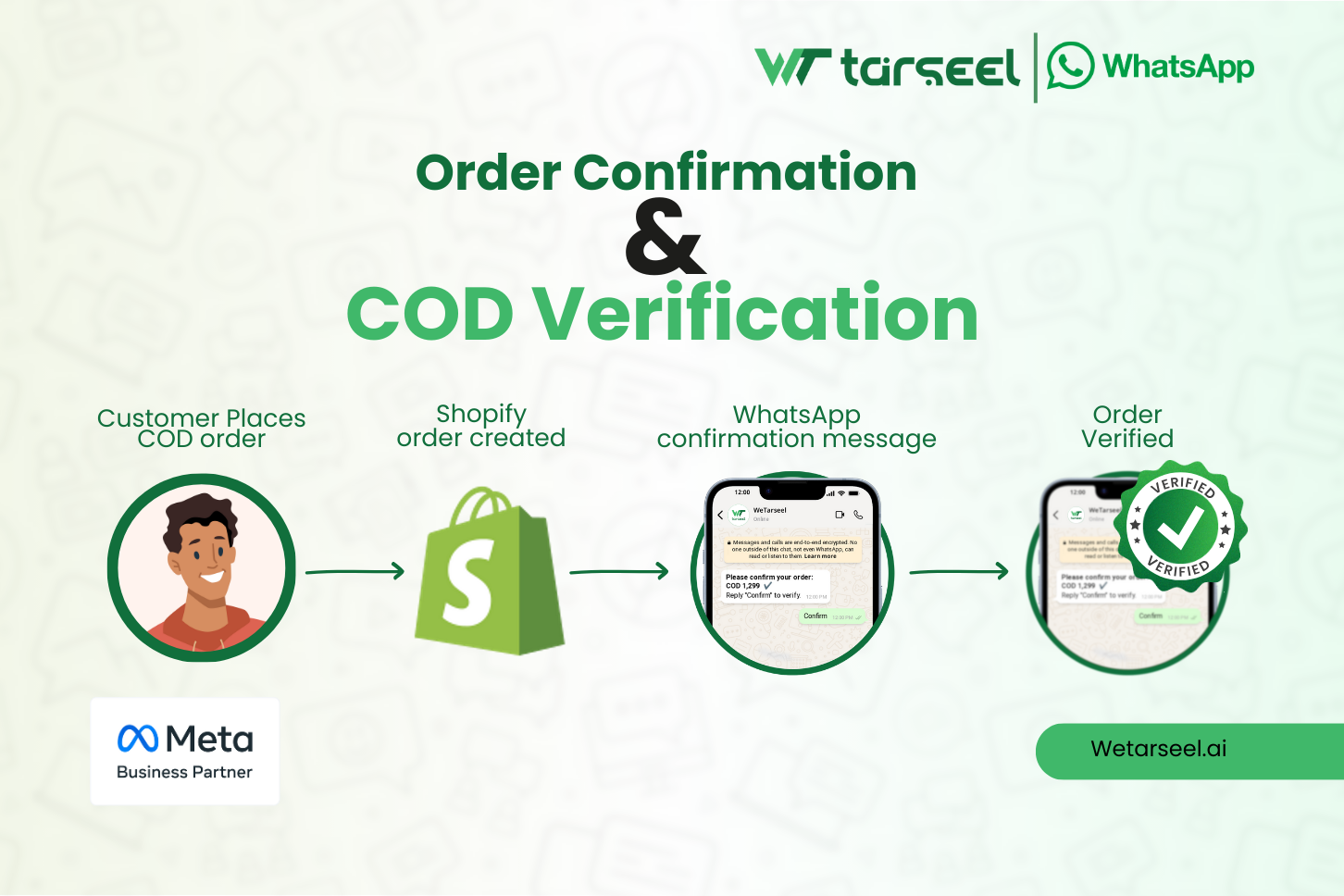
- Shopify sends order data immediately
- WhatsApp API triggers confirmation template
- Customer reply can be logged or routed
Operational impact:
- Fake orders filtered early
- Warehouse doesn’t ship unverified COD orders
- Cash flow improves
This is not a marketing use case — it’s risk control automation.
2- Abandoned Cart Recovery

Why WhatsApp works better technically:
- Real-time trigger (not scheduled batch)
- Deep-link back to checkout
- Message delivered during high intent window
Emails fail here because:
- Delayed delivery
- Low open rates
- Inbox clutter
WhatsApp wins because it matches timing with intent.
3- Post-Purchase Notifications
Examples:
- Order confirmed
- Shipped
- Out for delivery
Technical benefit:
- Reduces inbound support queries
- Offloads repetitive communication
- Keeps support teams focused on exceptions
This is a cost reduction mechanism, not just convenience.
WhatsApp API Pricing in Pakistan (How It Actually Works)
WhatsApp API pricing is:
- Conversation-based
- Defined by Meta
- Varies by message category (utility vs marketing)
Key points:
- No per-message spam pricing
- 24-hour customer service windows
- Template costs apply only for outbound initiation
Why this model exists:
- Discourages abuse
- Improves deliverability
- Rewards relevant communication
Cheap, unlimited messaging usually means policy violation risk.
Whatsapp API Pricing: All You Need to Know in 2025
Compliance Is Not Optional (And Why It Matters Long-Term)
WhatsApp enforces:
- Opt-in requirements
- Template approval
- Quality rating thresholds
Low-quality practices lead to:
- Reduced delivery
- Template rejection
- Account suspension
A proper provider focuses on:
- Message quality
- Flow design
- Long-term account health
Is WhatsApp API with Shopify Worth It for Pakistani Stores?
It is worth it if:
- You process daily orders
- You rely on COD
- You want predictable automation
- You value account safety
It is not worth it if:
- You want bulk blasting
- You avoid compliance
- You don’t plan to scale
This is an infrastructure decision, not a plugin experiment.
Final Take
WhatsApp API with Shopify in Pakistan works not because WhatsApp is popular, but because it integrates communication into the e-commerce system itself.
When implemented correctly, it becomes:
- A conversion stabilizer
- A trust amplifier
- A support cost reducer
The difference between success and failure lies in technical execution, compliance discipline, and understanding local ecommerce behavior, not in sending more messages.

WhatsApp API with Shopify in Pakistan: How It Works, Costs, and Real Ecommerce Use Cases

What is Template in WhatsApp (Marketing, Utility, Authentication)
Boost Sales with WhatsApp Catalogue: The Smart Seller’s Guide for 2026